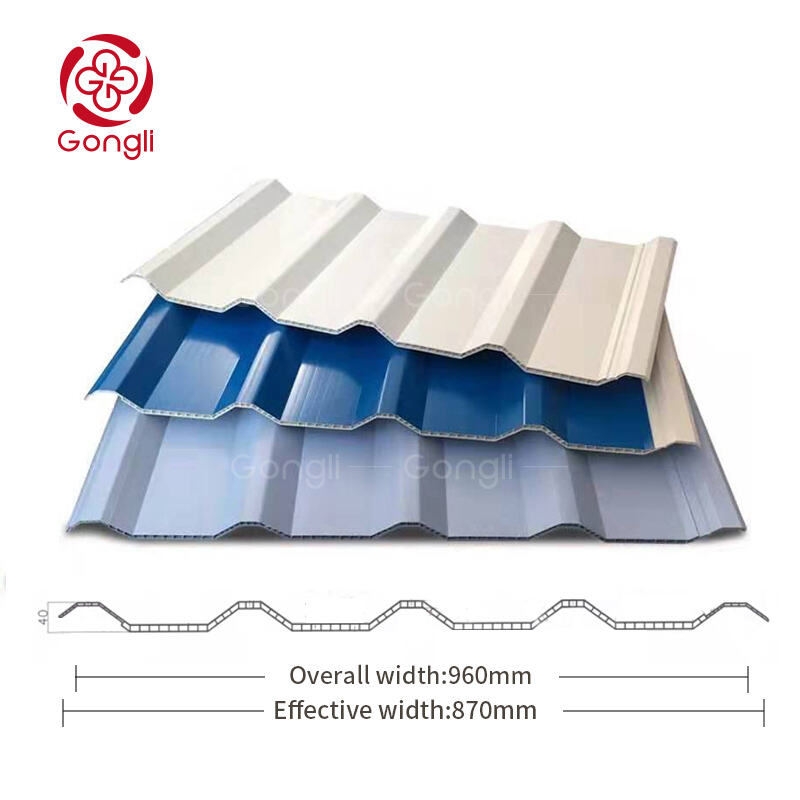
How do ASAPVC composite roof sheets compare with other roofing materials?
Material Composition and Structural Advantages of ASAPVC Composite Roof Sheets
Core components: The role of ASA, APVC, and PVC in composite roofing
ASAPVC composite roof sheets combine three different engineered polymers. First we have ASA or Acrylic-Styrene-Acrylonitrile which gives excellent resistance to UV damage. Then there's APVC, short for Acrylic Modified Polyvinyl Chloride, that handles chemicals pretty well. And finally regular old PVC adds some needed flexibility to the structure. When these materials work together, something interesting happens. The ASA surface actually bounces back around 92% of sunlight according to research from Polymer Engineering International in 2023. Meanwhile, the APVC part stands up to those harsh acids often found in factories and plants. What makes this composite approach special compared to just using one material? Well, it manages to stay strong over time while still dealing with temperature changes without warping too much. That balance is hard to achieve with traditional roofing options.
Layered construction for enhanced waterproofing and anti-corrosion performance
The 5-layer architecture of ASAPVC roofing delivers targeted performance through specialized strata:
| Layer | Function | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| ASA surface film | UV filtering & color retention | Maintains 95% reflectivity after 15 years |
| APVC reinforcement | Impact resistance | Withstands 120 mph winds |
| PVC core | Moisture barrier | 0% water absorption in lab tests |
This stratified structure reduces thermal expansion by 40% compared to conventional PVC sheets (2024 Composite Roofing Report), making it ideal for coastal factories exposed to salt spray and heavy monsoon rains.
ASAPVC vs. standard PVC roof sheets: Key differences in material science
Regular PVC sheets are basically just one layer thick, while ASAPVC adds surface hardened ASA and special APVC modifiers that boost tensile strength around three times over according to a study published last year in Material Science Quarterly. The improved formula stops the cracking and fading colors that happen to ordinary PVC within about five to seven years, so these upgraded sheets can last anywhere from 25 to 30 years even when exposed to harsh tropical conditions. What makes ASAPVC stand out even more is its ability to handle pH levels between 2 and 12. That's way better than regular PVC which only works safely between 4 and 9. For anyone working with chemicals, this wider tolerance range means ASAPVC becomes a much smarter choice for industrial applications where materials need to withstand tough environments day after day.
Durability and Weather Resistance in Challenging Environments
Performance under extreme conditions: Tropical, coastal, and industrial zones
ASAPVC composite roof sheets remain stable across temperatures from -30°C to 60°C, outperforming traditional metal roofing that begins to warp above 45°C (Institute of Building Materials 2023). In Southeast Asian industrial regions with annual rainfall exceeding 4,000mm, these composites maintain 99.7% water-tightness, surpassing galvanized steel alternatives at 94%.
UV resistance and long-term weatherability of ASAPVC versus traditional materials
The tri-layer ASA-PVC-PVC composition blocks 98% of UV radiation, significantly higher than the 82% offered by standard PVC. Field testing in Dubai (2016–2024) confirms that ASAPVC retains 92% of its original tensile strength after eight years—three times longer than conventional plastic roofing in high-solar-intensity environments.
Corrosion and salt spray resistance in high-humidity and marine environments
ASAPVC's molecular structure inhibits chloride ion penetration, enduring over 5,000 hours in salt spray tests (ASTM B117) without degradation. This performance exceeds powder-coated aluminum fencing solutions by 160% in corrosion resistance, a critical advantage in coastal areas where airborne salinity averages 3.5mg/m³.
Color stability and aesthetic longevity over time
ASAPVC sheets have something special going for them when it comes to color retention. With those advanced UV stabilizers built right in, these sheets keep about 98% of their original color after as long as 15 years on the roof, which actually meets the tough ISO 4892-3 standards. Compare that to ceramic coated metal roofs where we often see around 40% fading happening just within seven years alone. And there's another benefit too. These sheets come with a hydrophobic surface layer that really fights off dirt and pollutants sticking to them. Even in areas where air quality is poor and PM2.5 levels get above 75 micrograms per cubic meter, the solar reflectance stays pretty high at over 0.82 SR. That means buildings stay cooler naturally despite all the pollution hanging around outside.
Lifespan and Real-World Performance Compared to Traditional Roofing
Expected Service Life of ASAPVC vs. Metal, Asbestos, and Fiber Cement Roofs
ASAPVC composite roof sheets last around 25 to 35 years, which is better than asbestos that only lasts 15 to 20 years and fiber cement at 20 to 25 years. They come close to galvanized steel's impressive lifespan of 30 to 50 years too. According to industry studies from the 2023 Polymer Roofing Report, these ASA-PVC materials keep about 87% of their strength after twenty years on the roof. That's way ahead of regular PVC which drops to just 63% and even corrugated metal that manages only 71%. When looking at how different materials hold up over time, the numbers tell a pretty clear story about why many builders are turning to these composite options for long term durability.
| Material | Avg. Lifespan | Maintenance Cycle | UV Degradation Rate |
|---|---|---|---|
| ASAPVC Composite | 30+ years | 10–12 years | 0.8% annually |
| Galvanized Steel | 40–50 years | 5–7 years | Not applicable |
| Fiber Cement | 20–25 years | 3–5 years | 1.5% annually |
Long-Term Durability Evidence From Field Installations
Data from over 120 industrial sites shows only 2.7% of ASAPVC roofs required repairs within the first 15 years, compared to 18.4% for asbestos and 9.1% for coated metal roofs. In coastal Thailand, ASA-PVC installations maintained full waterproofing through 12 consecutive monsoon seasons, demonstrating superior resistance to moisture and corrosion relative to zinc-aluminum alloys.
Case Study: 15-Year Performance in Southeast Asian Industrial Parks
A 2022 evaluation of 47 warehouses using ASAPVC roofs in Malaysia's Klang Valley revealed:
- 0.03% annual color fade (vs. 0.12% for standard PVC)
- 92% reduction in condensation-related corrosion compared to metal roofs
- 64% lower lifecycle costs than fiber cement over 15 years
These outcomes align with global durability benchmarks for composite roofing, confirming ASAPVC's effectiveness in high-UV, high-humidity settings.
Maintenance Requirements and Total Cost of Ownership
Low maintenance needs of ASAPVC composite roof sheets
ASAPVC roofing systems cut down on all those regular maintenance headaches that come with older materials. Traditional metal roofs need constant anti-rust treatments while fiber cement options typically have to be sealed again every three to five years at minimum. The special ASA-PVC coating just keeps working without much fuss for years on end. According to research published last year in the field of construction materials, these composite roofs actually needed about 75 percent fewer repairs compared to standard galvanized steel alternatives during a ten year period. This is mainly because they naturally resist problems like mold growth, sun damage from UV rays, and harmful chemicals that would otherwise degrade most conventional roofing materials.
Cost-benefit analysis: Long-term value vs. corrugated metal and fiber cement
| Factor | ASAPVC Composite | Corrugated Metal | Fiber Cement |
|---|---|---|---|
| Initial Cost ($/m²) | 28-32 | 18-22 | 20-25 |
| Expected Lifespan | 25-30 years | 12-18 years | 15-20 years |
| Maintenance Cycle | None | 3-5 years | 5-8 years |
| 20-Year TCO ($/m²) | 34-38 | 52-68 | 48-60 |
According to the Roofing Materials Report 2023, ASAPVC composites deliver 22% lower total ownership costs than metal in high-humidity climates when accounting for replacement intervals and labor.
Industry trend: Growing adoption of low-maintenance composites in B2B construction
The market is looking at around 14% yearly growth when it comes to composite roofing on industrial buildings, according to forecasts coming out in 2024. Operators who care about their return on investment are leading this trend. Looking at actual numbers from 35 different logistics centers reported in the Facility Management Journal last year, we see warehouse managers cut down roof problems causing downtime by nearly half once they switched to composite roofing systems. What's happening here isn't just about one material choice but rather points to what the whole industry wants these days: building materials that don't need constant maintenance or replacement over time. Companies are starting to realize that spending a bit more upfront can save them headaches and money later on.
Optimal Application in Tropical and High-Humidity Climates
Thermal Performance and Moisture Management in Hot, Rainy Environments
ASAPVC Composite Roof Sheets perform really well in hot tropical climates. Tests show their surfaces stay about 42 degrees cooler than regular galvanized steel when exposed to the same amount of sunlight according to that recent Material Science study from 2024. What makes these sheets special is their three layer design. The top has this UV reflective coating called ASA while the middle layer wicks away moisture through PVC material. This combination helps cut down on those sudden humidity jumps inside buildings during heavy rains by around 30%. And there's something else too - built in drainage channels help move away most of the rainwater. Real world tests at resorts along the coasts of Southeast Asia found these channels handled nearly all the rainfall, keeping water from pooling on roofs.
Addressing Thermal Expansion and Condensation in Plastic-Based Roofing
The special polymer mix used in ASAPVC restricts linear expansion to just 0.8mm per meter when temperatures hit around 50°C, which is actually about 60% better than what we see with regular PVC materials. The system features interlocking joints that handle temperature changes really well while keeping those pesky seals intact. This design trick also gets rid of that annoying drumming sound metal roofs tend to make during intense tropical downpours. Speaking of moisture issues, there are tiny grooves underneath the material that stop condensation from building up over time. These micro-grooves help the product maintain its top performance standards, meeting the strict Class A vapor transmission requirements set forth by ASTM E96 testing protocols.
Strategic Selection of Roofing Materials for Monsoon and High-Solar-Gain Regions
For high-humidity, high-solar regions, key selection criteria include:
- Solar reflectance: ASAPVC maintains 89% reflectivity after 10 years vs. 62% for painted metal
- Wind uplift resistance: Certified to withstand 160kph winds (AS/NZS 1562.3)
- Maintenance frequency: 87% fewer cleaning requirements than porous cement sheets
Installation records from 23 equatorial projects show a 2.1% defect rate over five years for ASAPVC systems, far below the 11.8% observed for metal and cement composites. These results establish ASAPVC as the preferred choice for hospitals, warehouses, and agricultural facilities operating in demanding tropical climates.
FAQ Section
What are the main materials used in ASAPVC composite roof sheets?
ASAPVC composite roof sheets consist of ASA, APVC, and PVC, combining the best properties of each material for superior performance.
How does ASAPVC compare to standard PVC sheets?
ASAPVC provides significantly better resistance to UV radiation, chemicals, and temperature fluctuations, with a lifespan of 25-30 years, compared to the 5-7 years of standard PVC sheets.
What makes ASAPVC ideal for use in tropical and high-humidity climates?
ASAPVC sheets are designed to handle challenges like high temperatures, humidity, and heavy rains with their UV reflective coatings, moisture-wicking layers, and built-in drainage channels.
Recommended Products
Hot News
-
How to choose the right roof tile
2024-01-24
-
PVC Plastic Tiles: The Ideal Roofing Material
2024-01-24
-
The Essentials of Synthetic Resin Tile Manufacturing
2024-01-24

 EN
EN
 AR
AR
 BG
BG
 HR
HR
 CS
CS
 DA
DA
 NL
NL
 FI
FI
 FR
FR
 DE
DE
 EL
EL
 HI
HI
 IT
IT
 JA
JA
 KO
KO
 NO
NO
 PL
PL
 PT
PT
 RO
RO
 RU
RU
 ES
ES
 TL
TL
 IW
IW
 ID
ID
 LT
LT
 VI
VI
 TH
TH
 TR
TR
 AF
AF
 MS
MS
 KM
KM
 LO
LO
 MY
MY